Mastering Simple Present vs Present Continuous: Your Essential Guide
Welcome to your guide to two of the most fundamental tenses in English: the Simple Present and the Present Continuous. Don’t worry if they seem a bit tricky at first; by the end of this article, you’ll be using them like a pro!
We’ll break down each tense with lots of clear examples and handy charts. We’ll also explore why understanding these tenses is so important and how they’re used in real life. Ready? Let’s dive in!
Why Are These Tenses Important?
Learning the Simple Present and Present Continuous is like learning the basic building blocks of English sentences. They help you:
- Talk about yourself and your daily life: “I live in Cambodia.” “I am studying English.”
- Describe what’s happening right now: “The sun is shining.”
- Share facts and general truths: “Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.”
- Understand native speakers better: These tenses are used constantly in everyday conversation, movies, and books.
By mastering them, you’ll feel more confident in expressing yourself and understanding others – a crucial step in your English journey!
Simple Present: What It Is and How to Use It
The Simple Present tense is used for actions that happen regularly, are always true, or are facts. Think of it as describing habits, routines, and general statements.
When to Use the Simple Present:
- Habits and Routines: Actions you do again and again.
- I wake up at 7 AM every day.
- She drinks coffee in the morning.
- They play football on Saturdays.
- General Truths and Facts: Things that are always true.
- The Earth goes around the Sun.
- Water freezes at 0 degrees Celsius.
- Birds fly.
- Scheduled Events (Future): For things that are fixed on a timetable or schedule.
- The train leaves at 3 PM.
- The movie starts at 8 PM.
- My class finishes at noon.
Simple Present Form (How to Make It):
The basic form is the base form of the verb.
- Subject + Verb (base form)
Important Note for He/She/It (Third Person Singular): For “he,” “she,” and “it,” we add an “-s” or “-es” to the end of the verb.
| Subject | Verb (base form) | Example |
| I | speak | I speak English. |
| You | speak | You speak English. |
| We | speak | We speak English. |
| They | speak | They speak English. |
| He | speaks | He speaks English. |
| She | speaks | She speaks English. |
| It | speaks | It speaks English. |
Making Simple Present Negative:
We use “do not” (don’t) or “does not” (doesn’t) + base form of the verb.
- I do not (don’t) like spiders.
- He does not (doesn’t) play tennis.
- They do not (don’t) live in France.
Asking Simple Present Questions:
We use “Do” or “Does” at the beginning of the question + subject + base form of the verb.
- Do you speak English?
- Does she work on weekends?
- Do they have a car?
Present Continuous: What It Is and How to Use It
The Present Continuous tense (also called Present Progressive) is used for actions happening right now, at this moment, or around this moment. It describes temporary actions.
When to Use the Present Continuous:
- Actions Happening Now: What you are doing at the exact moment you are speaking.
- I am writing an article. (Happening now)
- You are reading this guide. (Happening now)
- They are watching TV. (Happening now)
- Temporary Actions: Actions that are happening for a limited time, even if not at this exact second.
- He is studying a lot for his exams this week. (He might not be studying at this very second, but it’s a temporary activity.)
- I am working on a big project these days.
- She is living with her aunt this month.
- Changing or Developing Situations:
- The weather is getting warmer.
- Your English is improving!
Present Continuous Form (How to Make It):
The form is “to be” verb (am, is, are) + verb + “-ing”.
- Subject + am/is/are + Verb (-ing)
| Subject | To Be Verb | Verb (-ing) | Example |
| I | am | speaking | I am speaking now. |
| You | are | speaking | You are speaking now. |
| We | are | speaking | We are speaking now. |
| They | are | speaking | They are speaking now. |
| He | is | speaking | He is speaking now. |
| She | is | speaking | She is speaking now. |
| It | is | speaking | It is speaking now. |
Making Present Continuous Negative:
We add “not” after “am,” “is,” or “are.”
- I am not (I’m not) working right now.
- He is not (isn’t) listening to music.
- They are not (aren’t) playing outside.
Asking Present Continuous Questions:
We put “Am,” “Is,” or “Are” at the beginning of the question + subject + verb + “-ing.”
- Are you studying English?
- Is he cooking dinner?
- Are they waiting for the bus?
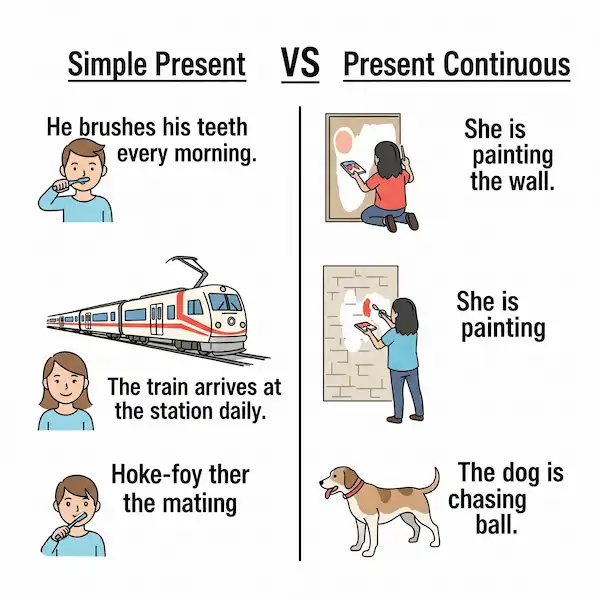
Simple Present vs. Present Continuous: The Big Difference!
This is where it all comes together! The main difference is whether the action is regular/habitual/fact (Simple Present) or happening right now/temporary (Present Continuous).
Let’s look at some direct comparisons:
| Simple Present (Habits, Facts, Routines) | Present Continuous (Happening Now, Temporary) |
| I drink coffee every morning. (A habit) | I am drinking coffee now. (Happening at this moment) |
| She works in an office. (Her regular job) | She is working from home today. (Temporary action) |
| They usually play soccer on Sundays. (A routine) | They are playing soccer in the park right now. (Happening at this moment) |
| The sun rises in the East. (A fact) | Look! The sun is rising! (Happening at this moment) |
| We go to school five days a week. (A routine) | We are going to the cinema tonight. (A planned, temporary action) |
Common Time Expressions
Certain words and phrases often go with one tense or the other. These are great clues!
Time Expressions for Simple Present:
- Always, usually, often, sometimes, rarely, never (frequency)
- Every day/week/month/year
- On Mondays/Tuesdays, etc.
- In the morning/afternoon/evening
- At night
Time Expressions for Present Continuous:
- Now, right now
- At the moment
- Today, this week/month/year (for temporary actions)
- Currently
- Look! Listen! (Often signal something happening right now)
Verbs That Usually Don’t Use the Continuous Form (Stative Verbs)
This is a bit more advanced, but very helpful! Some verbs describe states, thoughts, emotions, or senses, not actions. These “stative verbs” are usually NOT used in the Present Continuous.
Examples of Stative Verbs:
- Emotions: love, hate, like, want, need, prefer
- Correct: I love pizza.
- Incorrect: I am loving pizza.
- Senses: hear, see, smell, taste, feel (when describing a sensation, not an action)
- Correct: I hear music.
- Incorrect: I am hearing music.
- Thoughts/Opinions: know, believe, understand, think (when it means “believe”), remember, forget, agree
- Correct: I know the answer.
- Incorrect: I am knowing the answer.
- Possession: have (when it means “possess”), own, belong
- Correct: I have a car.
- Incorrect: I am having a car. (Note: “I am having dinner” is correct because “having” is part of an action here.)
Why is this important? Using these verbs in the continuous form can sound unnatural to native speakers.
Putting It All Together: Practice Makes Perfect!
The best way to master these tenses is to practice!
- Describe your daily routine: Use the Simple Present. “I wake up, I eat breakfast, I go to work…”
- Describe what’s happening around you right now: Use the Present Continuous. “The birds are singing, my neighbor is walking his dog, I am sitting at my desk…”
- Listen to English music and podcasts, watch movies: Pay attention to how native speakers use these tenses. Can you identify why they chose one over the other?
Conclusion
You’ve done a fantastic job exploring the Simple Present and Present Continuous! Remember:
- Simple Present: For habits, routines, and facts.
- Present Continuous: For actions happening now or temporarily.
Keep practicing, keep noticing, and don’t be afraid to make mistakes – they are part of learning! You are well on your way to becoming a confident English speaker.
Additional Helpful Content
Story Time! (Applying the Tenses)
Let’s read a short story and see how both tenses are used:
“Every morning, John wakes up at 6 AM. He eats a quick breakfast and then goes for a run. Right now, it’s 7 AM. John is running in the park, and he is listening to his favorite music. Usually, he sees many people, but today, it’s raining, so he is running alone. He doesn’t like running in the rain, but he is training for a marathon, so he needs to practice every day. Later, he will go to work. His office is located downtown. He often has meetings in the afternoon.”
Can you see how the Simple Present tells us about John’s usual routine, while the Present Continuous tells us what he is doing right now and temporarily?
Self-Correction Tip for Beginners
When you’re speaking, pause and ask yourself:
- “Is this something I do every day or all the time?” (Simple Present)
- “Is this something I am doing at this exact moment?” (Present Continuous)
This simple thought process can help you choose the correct tense.
Practice makes perfect
Here is a PDF worksheet you can download with 25 practice sentences using simple present or present continuous. The answers are on a separate sheet.
Additional Helpful Information
- The verb To Be is a very important subject to understand – The Verb ‘To Be’: Essential English for Beginners
External Links for Authoritative Sources
To continue your learning and verify information, here are some highly respected resources:
- British Council LearnEnglish: A fantastic resource with explanations, exercises, and games.
- Cambridge Dictionary Grammar: Offers clear explanations and examples.
- Purdue OWL (Online Writing Lab): A widely recognized academic resource for English grammar and writing.
- Verb Tenses (Look for “Simple Present” and “Present Progressive”)
Happy learning!