Understanding Present and Past Participles in English 🧐
Welcome, intermediate English learners! Today, we’re going to explore two important verb forms: present participles and past participles. Understanding these will significantly improve your English grammar and help you express yourself more clearly. Let’s dive in!
What are Participles? 🤔
Participles are verb forms that act like adjectives. They can describe nouns and pronouns. There are two main types:
- Present Participles: Usually end in -ing verb
- Past Participles: Often end in -ed, but can have irregular forms (like gone, eaten, broken).
Present Participles (-ing forms) 🏄♀️
Present participles have several important uses:
1. Forming Continuous Verb Tenses: They are essential for the present continuous, past continuous, future continuous, and present perfect continuous tenses.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
| Present Continuous | is/am/are + -ing | I am studying English right now. |
| Past Continuous | was/were + -ing | She was reading when I called. |
| Future Continuous | will be + -ing | They will be traveling next month. |
| Present Perfect Continuous | have/has been + -ing | He has been working here for five years. |
2. Acting as Adjectives: They can describe nouns, telling us more about their qualities or actions.
- The barking dog kept me awake. (barking describes the dog)
- We saw a flying bird. (flying describes the bird)
- She gave me a smiling face. (smiling describes the face)
3. Forming Gerunds: While similar in form, when a present participle acts as a noun, it’s called a gerund.
- Swimming is good exercise. (Swimming is the subject of the sentence)
- She enjoys reading. (reading is the object of the verb enjoys)
Past Participles (usually -ed, or irregular forms) 🧑🍳
Past participles also have crucial roles in English grammar:
1. Forming Perfect Verb Tenses: They are used with have, has, and had to create the present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect tenses.
| Tense | Structure | Example |
| Present Perfect | have/has + past participle | I have finished my homework. |
| Past Perfect | had + past participle | They had eaten before we arrived. |
| Future Perfect | will have + past participle | She will have graduated by next year. |
2. Forming the Passive Voice: Past participles are used with forms of the verb to be (is, am, are, was, were, been, being) to create passive sentences.
- The window was broken.
- The letter was written by my friend.
- The cake has been eaten.
3. Acting as Adjectives: Similar to present participles, they can describe nouns.
- He wore a torn shirt. (torn describes the shirt)
- She found a lost key. (lost describes the key)
- The spoken words were kind. (spoken describes the words)
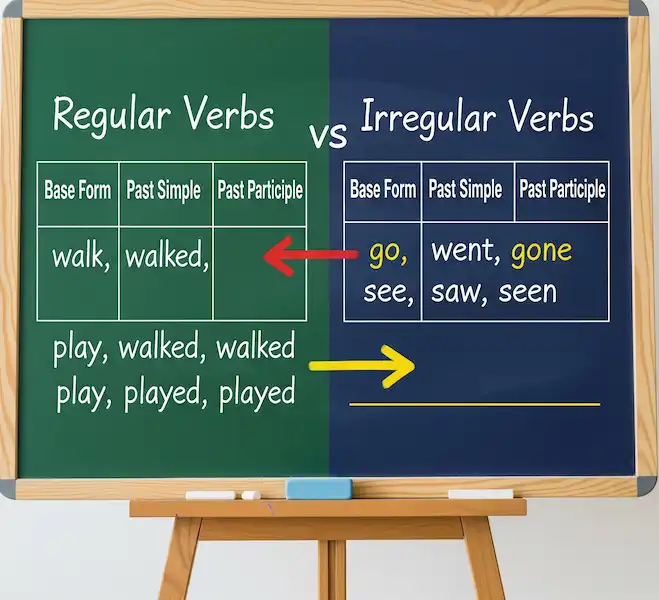
Irregular Past Participles: Remember that many verbs have irregular past participle forms. Here are a few common examples:
| Base Verb | Past Simple | Past Participle |
| go | went | gone |
| eat | ate | eaten |
| see | saw | seen |
| break | broke | broken |
| write | wrote | written |
| take | took | taken |
You’ll need to learn these through practice and exposure to English. Don’t worry, you’ll get the hang of it! 💪
Additional Tips ✨
Distinguishing Between Present and Past Participles as Adjectives:
- Present participles often describe something that causes a feeling or action.
- That was a boring movie. (The movie caused boredom.)
- The exciting news made everyone happy. (The news caused excitement.)
- Past participles often describe something that experiences a feeling or action.
- I was bored during the movie. (I experienced boredom.)
- They were excited about the news. (They experienced excitement.)
Chart Summary:
| Feature | Present Participle (-ing) | Past Participle (-ed / irregular) |
| Tenses | Continuous tenses | Perfect tenses, Passive voice |
| Adjective Use | Describes causing action/feeling | Describes experiencing action/feeling |
| Example (Tense) | They are eating. | They have eaten. |
| Example (Adj.) | a running child | a broken toy |
Web Article Content
For students preparing for English language assessments, understanding participles is essential. You will likely encounter questions that test your ability to:
- Identify the correct verb tense, which requires recognizing present and past participles.
- Form grammatically correct sentences using continuous and perfect tenses, as well as the passive voice.
- Understand the function of participles as adjectives.
- Differentiate between present participles and gerunds.
Practice Makes Perfect
Practice Tip: Pay close attention to the auxiliary verbs (is, are, was, were, have, has, had, will be, etc.) as they often indicate which tense or voice is being used and therefore which participle form is needed.
Example Question:
Choose the correct verb form to complete the sentence:
The children ________ (play) football in the park when it started to rain.
a) are playing b) played c) were playing d) have played
Answer: c) were playing (past continuous tense requires the present participle playing with the auxiliary verbs were)
Here is a PDF worksheet you can download to practice forming sentences using present and past participles. The answers are on a separate page.
Additional Helpful Content
- Learn about past tense phrasal verbs – Mastering Past Tense Phrasal Verbs: A Simple Guide
External Links for Further Learning 🔗
- British Council – Learn English: https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/english-grammar-reference/present-participle
- British Council – Learn English: https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/grammar/english-grammar-reference/past-participle
- Khan Academy – Verb Forms: https://www.khanacademy.org/humanities/grammar/parts-of-speech-the-verb/verb-forms/v/present-and-past-participles
These resources offer more detailed explanations and exercises to help you master present and past participles. Keep practicing, and you’ll become more confident in your English skills! 😊