Mastering Past Tense Phrasal Verbs in English 💪
Today, we’re going to tackle a super useful part of English: past tense phrasal verbs. Don’t worry, it’s not as scary as it sounds! Phrasal verbs are just verbs combined with a preposition or an adverb, like “up,” “out,” or “for.” They often have meanings different from the individual words. Let’s dive in!
What are Phrasal Verbs? 🤔
Think of phrasal verbs as mini word combinations that have their own special meaning.
Verb + Preposition/Adverb = Phrasal Verb
Here are a few examples:
- look (to use your eyes) + up (towards a higher place) = look up (to try and find information in a book or on the internet)
- go (to move from one place to another) + out (away from the inside of a place) = go out (to leave a place to go somewhere else)
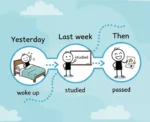
- wake (to stop sleeping) + up (from a state of sleep) = wake up (to stop sleeping)
Why are Past Tense Phrasal Verbs Important? 🗣️
When you talk about things that happened before now, you need to use the past tense. Just like regular verbs change their form in the past tense (e.g., “walk” becomes “walked”), phrasal verbs also need to be in the past tense. Knowing how to use them correctly will make your English sound more natural and fluent!
Common Past Tense Phrasal Verbs with Examples 📝
Here’s a chart of some common phrasal verbs in the past tense with example sentences to help you understand how to use them:
| Present Tense Phrasal Verb | Past Tense Phrasal Verb | Meaning | Example Sentence |
| wake up | woke up | to stop sleeping | I woke up early this morning. |
| get up | got up | to stand up after sitting or lying down | She got up from the chair. |
| go out | went out | to leave a place to go somewhere else | They went out for dinner last night. |
| come back | came back | to return to a place | He came back home late. |
| look for | looked for | to try to find something | I looked for my keys everywhere. |
| find out | found out | to discover information | We found out about the party yesterday. |
| turn on | turned on | to start a machine or light | He turned on the television. |
| turn off | turned off | to stop a machine or light | She turned off the lights before leaving. |
| put on | put on | to dress yourself | He put on his jacket because it was cold. |
| take off | took off | to remove clothing or for a plane to leave the ground | She took off her shoes when she entered the house. |
| give up | gave up | to stop trying to do something | I gave up trying to solve the puzzle. |
| break down | broke down | to stop working (for a machine) | The car broke down on the way to Phnom Penh. |
| grow up | grew up | to become an adult | She grew up in Siem Reap. |
| eat out | ate out | to eat at a restaurant | We ate out at a nice restaurant last weekend. |
| call off | called off | to cancel something | They called off the meeting due to the rain. |
Regular vs. Irregular Phrasal Verbs ⚠️
Just like regular verbs, some phrasal verbs form their past tense by adding “-ed” (or “-d”), while others are irregular and have different past tense forms.
Regular (add -ed/-d):
- look up -> looked up
- turn on -> turned on
- call off -> called off
Irregular (change spelling):
- wake up -> woke up
- go out -> went out
- come back -> came back
- find out -> found out
- take off -> took off
- eat out -> ate out
Important Note: The preposition or adverb in the phrasal verb usually doesn’t change in the past tense. Only the verb part changes.
Focus on Context! 💡
When you learn new phrasal verbs, try to learn them in context. Read sentences and stories that use them. This will help you understand their meaning and how they are used correctly in the past tense. Pay attention to the words that come before and after the phrasal verb.
Separable vs. Inseparable Phrasal Verbs 🧱🔗
Some phrasal verbs can be separated by the object, while others cannot.
Separable: The object can go between the verb and the preposition/adverb.
- Present: Can you turn the light on? OR Can you turn on the light?
- Past: He turned the television on. OR He turned on the television.
Inseparable: The object must come after the preposition/adverb.
- Present: We need to look after our younger siblings. (NOT: We need to look our younger siblings after.)
- Past: They looked after their grandmother last year.
Tip: It’s helpful to learn whether a phrasal verb is separable or inseparable when you learn the phrasal verb itself.
Putting It All Together: Practice Time! ✍️
Fill in the blanks with the correct past tense form of the phrasal verb in parentheses:
- Yesterday morning, I ___________ (wake up) feeling refreshed.
- They ___________ (go out) to the cinema on Saturday night.
- She ___________ (look for) her phone but couldn’t find it.
- We ___________ (find out) the results of the exam last week.
- He ___________ (turn on) the fan because it was hot.
Answers to the Practice Time:
- woke up
- went out
- looked for
- found out
- turned on
Here us a PDF worksheet you can download with 25 practice questions for studying phrasal verbs. The answers are on a separate page.
Additional Helpful Content
- Study more modal verbs, could, would, should – Could Would Should Explained: A Simple Guide
- Learn how to use Present and Past Participles – Present and Past Participles Explained
External Links for Further Learning 🌐
- BBC Learning English – Phrasal Verbs: https://www.bbc.co.uk/learningenglish/english/course/lower-intermediate/unit-23/session-1
- British Council – LearnEnglish – Phrasal Verbs: https://learnenglish.britishcouncil.org/english-grammar/phrasal-verbs
Conclusion 🎉
Learning past tense phrasal verbs takes practice, but it’s a crucial step in improving your English fluency. Keep practicing with the examples and remember to pay attention to how native speakers use them. Good luck with your English studies!