Introduction: The World of English Plurals
Welcome, intermediate English learners! You’ve likely mastered the basic rule of adding “-s” or “-es” to make most nouns plural. (Think “cat” to “cats,” or “box” to “boxes.”) But English, being the wonderfully quirky language it is, loves to throw in exceptions! These exceptions are called irregular plurals, and they don’t follow the standard rules.
Don’t worry, you’re not alone if these nouns sometimes trip you up. Even native speakers pause occasionally! This comprehensive guide will help you understand and conquer 20 of the most common irregular plural nouns, boosting your confidence and accuracy in English.
Why Do We Have Irregular Plurals? (A Little History Lesson)
Understanding why these irregularities exist can actually make them easier to remember. Many irregular plurals are relics of Old English and other historical influences. While the language evolved and mostly standardized its plural forms, some words held onto their ancient plural spellings. It’s a fascinating peek into the history of the English language!
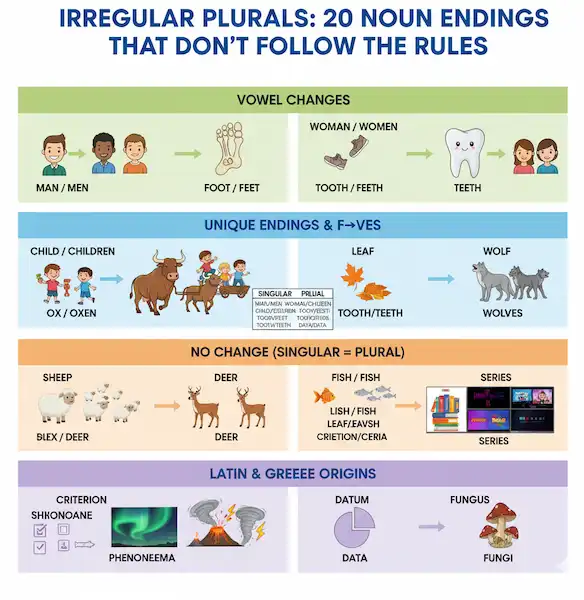
The 20 Irregular Plural Nouns You Need to Know
Let’s dive into the list! We’ll categorize them to make learning even easier.
Category 1: Vowel Changes in the Middle
These words change one or more vowels in their singular form to become plural.
- Man / Men
- Singular: A single man
- Plural: Two men
- Example: The man walked to the store. The men played football.
- Tip: Think of “men” as an older, stronger version of “man.”

- Woman / Women
- Singular: One woman (pronounced WOO-mun)
- Plural: Several women (pronounced WIM-in)
- Example: A woman sang beautifully. The women discussed the book.
- Tip: Notice the pronunciation change in the plural!
- Foot / Feet
- Singular: One foot
- Plural: Two feet
- Example: My left foot hurts. I have two feet.
- Tooth / Teeth
- Singular: One tooth
- Plural: Many teeth
- Example: The baby has one new tooth. Brush your teeth twice a day.
- Goose / Geese
- Singular: A lone goose
- Plural: A flock of geese
- Example: A white goose swam in the pond. We saw many geese flying south.
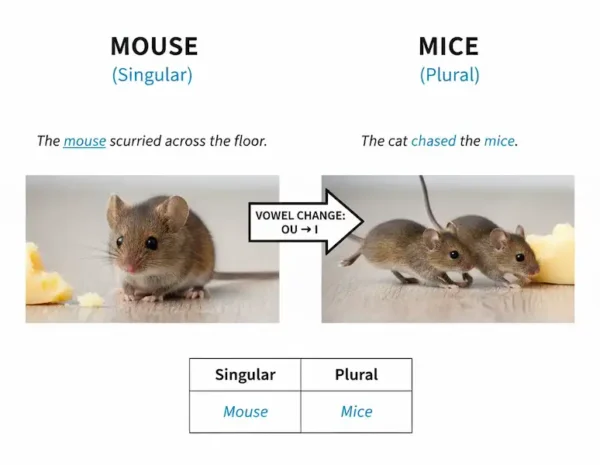
- Mouse / Mice
- Singular: A little mouse
- Plural: A group of mice
- Example: The mouse scurried across the floor. The cat chased the mice.
Category 2: Adding “-en” or Changing “f” to “v”
These words have unique endings or sound changes.
- Child / Children
- Singular: One child
- Plural: Many children
- Example: The child played with a toy. The children laughed happily.
- Tip: This is one of the most common and important ones to remember!
- Ox / Oxen
- Singular: An ox (a type of cattle)
- Plural: A pair of oxen
- Example: The farmer used an ox to pull the plow. A team of oxen moved the heavy cart.
- Note: This word is less common in everyday conversation but good to know.
- Leaf / Leaves
- Singular: A green leaf
- Plural: Many fallen leaves
- Example: A single leaf fell from the tree. In autumn, the leaves change color.
- Rule: Many nouns ending in “-f” or “-fe” change to “-ves” in the plural (e.g., knife/knives, wife/wives).
- Wolf / Wolves
- Singular: A lone wolf
- Plural: A pack of wolves
- Example: A wolf howled at the moon. The wolves hunted together.
Category 3: Nouns That Don’t Change (Same Singular & Plural)
These are tricky because the word stays exactly the same, whether you’re talking about one or many. Context is key here!
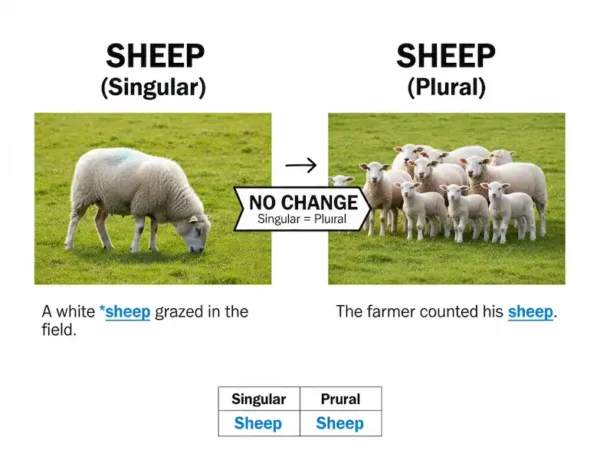
- Sheep / Sheep
- Singular: One sheep
- Plural: Many sheep
- Example: A white sheep grazed in the field. The farmer counted his sheep.
- Fish / Fish * Singular: One fish * Plural: A school of fish * Example: I caught a large fish. There are many fish in the ocean. * Note: “Fishes” can sometimes be used when referring to different species of fish, but “fish” is the standard plural.
- Deer / Deer
- Singular: A wild deer
- Plural: A herd of deer
- Example: We saw a deer in the forest. Several deer ran across the road.
- Series / Series
- Singular: A new TV series
- Plural: Several book series
- Example: That new TV series is very popular. I’ve watched all the series by that director.
- Species / Species
- Singular: A rare species
- Plural: Many different species
- Example: Pandas are an endangered species. The island is home to unique species of birds.
Category 4: Nouns from Latin & Greek (Ending Changes)
These words often come from other languages and keep their original plural forms.
- Criterion / Criteria
- Singular: One criterion (a standard by which something is judged)
- Plural: Many criteria
- Example: What is the main criterion for success? We have several criteria for evaluating applicants.
- Phenomenon / Phenomena
- Singular: A strange phenomenon (an observable fact or event)
- Plural: Natural phenomena
- Example: The aurora borealis is a beautiful phenomenon. Earthquakes and tsunamis are natural phenomena.
- Datum / Data
- Singular: A single datum (a piece of information)
- Plural: Multiple data (collection of facts)
- Example: This datum supports my theory. The data shows a clear trend.
- Note: In modern English, “data” is very commonly treated as both singular and plural (e.g., “the data is accurate” or “the data are accurate”). However, for formal writing, remember “datum” is singular.
- Fungus / Fungi (or Funguses)
- Singular: One fungus
- Plural: Many fungi (pronounced FUN-jy) or funguses
- Example: A strange fungus grew on the tree. The forest floor was covered in diverse fungi.
- Tip: “Fungi” is generally preferred in scientific contexts.
- Nucleus / Nuclei
- Singular: The nucleus (central part of an atom/cell)
- Plural: Multiple nuclei (pronounced NOO-klee-eye)
- Example: Each atom has a nucleus. The cells contain multiple nuclei.
Chart Summary of Irregular Plurals
Here’s a quick reference chart to help you review!
| Singular | Plural | Category |
| Man | Men | Vowel Change |
| Woman | Women | Vowel Change |
| Foot | Feet | Vowel Change |
| Tooth | Teeth | Vowel Change |
| Goose | Geese | Vowel Change |
| Mouse | Mice | Vowel Change |
| Child | Children | Unique Ending |
| Ox | Oxen | Unique Ending |
| Leaf | Leaves | F to V + es |
| Wolf | Wolves | F to V + es |
| Sheep | Sheep | No Change |
| Fish | Fish | No Change |
| Deer | Deer | No Change |
| Series | Series | No Change |
| Species | Species | No Change |
| Criterion | Criteria | Latin/Greek (on -> a) |
| Phenomenon | Phenomena | Latin/Greek (on -> a) |
| Datum | Data | Latin/Greek (um -> a) |
| Fungus | Fungi | Latin/Greek (us -> i) |
| Nucleus | Nuclei | Latin/Greek (us -> i) |
Tips for Mastering Irregular Plurals
- Read and Listen Actively: The more you expose yourself to English, the more naturally these forms will stick. Pay attention to how native speakers use them.
- Practice, Practice, Practice: Use flashcards, quizzes, or create your own sentences. Repetition is key!
- Group Them: As we did in this article, grouping similar irregular plurals can aid memorization.
- Don’t Be Afraid to Make Mistakes: Everyone makes mistakes! The important thing is to learn from them.
- Focus on the Most Common Ones First: Start with “man/men,” “woman/women,” “child/children,” “foot/feet,” and “tooth/teeth.” You’ll encounter these most often.
- Context is Your Friend: For words like “sheep” or “fish,” the surrounding words (e.g., “one sheep” vs. “many sheep”) will tell you if it’s singular or plural.
FAQs about Irregular Plurals
Q: Are there any other patterns for irregular plurals not covered here? A: Yes, there are some less common ones, and also words that came from other languages (like “cactus/cacti” or “octopus/octopi/octopuses”). However, the 20 covered here are among the most frequently used.
Q: Is “fishes” ever correct? A: “Fishes” can be used when referring to different types or species of fish. For example, “The aquarium contained many colorful fishes.” However, if you’re talking about multiple individual fish of the same kind, “fish” is the standard plural: “I caught three fish.”
Q: What about words like “media” and “alumni”? A: These are also irregular plurals from Latin. “Media” is the plural of “medium,” and “alumni” is the plural of “alumnus” (male graduate) or “alumna” (female graduate). These follow similar patterns to “data” and “criteria.”
Q: How can I tell if a word is irregular or not? A: Unfortunately, there’s no simple rule to identify irregular plurals just by looking at the singular form. The best way is to learn them as you encounter them. If you’re unsure, a dictionary is always your best friend!
Conclusion: You’ve Got This!
Learning irregular plurals takes time and practice, but it’s a vital step in becoming a more fluent and accurate English speaker. By understanding the common patterns and committing these 20 words to memory, you’re well on your way to mastering one of English’s charming complexities. Keep practicing, and soon these irregular forms will feel completely natural to you!
Practice Makes Perfect
Here is a PDF worksheet you can download to practice about irregular plurals. The answers are on a separate page.
Additional Helpful Links
Study about proper noun capitalization – Proper Noun Capitalization Rules: A Guide for Writers
External Authoritative Sources for Further Learning
- Purdue OWL (Online Writing Lab) – Irregular Plural Nouns: A highly respected resource for all aspects of English grammar.
- University College London (UCL) – Guide to Grammar: Offers detailed explanations on various grammar topics, including plural forms.
- https://www.ucl.ac.uk/language-centre/resources/english-grammar-guide/nouns (You may need to navigate to the plurals section within the noun guide).
- Merriam-Webster Learner’s Dictionary: An excellent resource for checking specific word forms and understanding their usage.
- https://www.learnersdictionary.com/ (Search for individual words and check their plural forms).