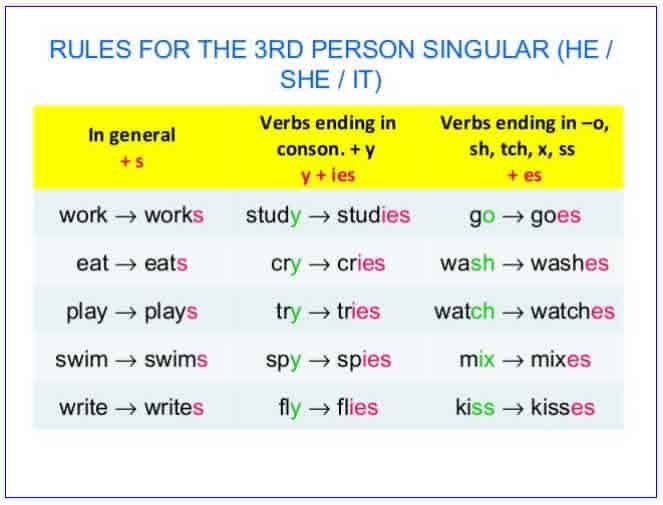
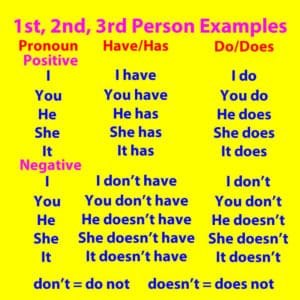
Learning About “Have/Has,” “Do/Does,” and “Don’t/Doesn’t”
Today, we’re going to tackle some of the most common and useful words in the English language: have/has, do/does, and don’t/doesn’t. These little words might seem tricky at first, but with a little practice, you’ll be using them like a pro!
Why Are These Words So Important?
“Have/Has” helps us talk about possession (what someone owns) or experiences. “Do/Does” is vital for asking questions and making negative statements. Mastering these words is a foundational step to building clear and correct English sentences. Native speakers use them all the time, so understanding them will significantly improve your listening and speaking skills!
1. Have vs. Has: What You Own and What You’ve Experienced
“Have” and “has” are both forms of the verb “to have.” We use them to show possession (that something belongs to someone) or to talk about experiences and characteristics. The key difference is who you are talking about!
Who uses “Have”?
We use have with:
- I (first person singular)
- You (second person singular and plural)
- We (first person plural)
- They (third person plural)
- Plural nouns (e.g., “the students,” “my friends”)
Who uses “Has”?
We use has with:
- He (third person singular male)
- She (third person singular female)
- It (third person singular neutral/object)
- Singular nouns (e.g., “the dog,” “my sister,” “John”)
Let’s See Some Examples!
| Subject | Verb | Object/Experience | Example Sentence | Meaning |
| I | have | a new book | I have a new book. | I own a new book. |
| You | have | a great idea | You have a great idea. | You possess a great idea. |
| We | have | fun together | We have fun together. | We experience fun. |
| They | have | a big house | They have a big house. | They own a big house. |
| The students | have | homework | The students have homework. | Homework is assigned to them. |
| He | has | a red car | He has a red car. | He owns a red car. |
| She | has | long hair | She has long hair. | Her hair is long. |
| It | has | sharp teeth | It has sharp teeth. | The animal has sharp teeth. |
| My sister | has | a good job | My sister has a good job. | She is employed in a good job. |
Chart for “Have” vs. “Has”
| Subject | Verb |
| I | have |
| You | have |
| We | have |
| They | have |
| Plural Nouns | have |
| He | has |
| She | has |
| It | has |
| Singular Nouns | has |
We speak using first person, second person and third person pronouns. Here is a definition of the different Persons:

This is an example of a conversation using all three Persons:

2. Do vs. Does: Asking Questions and Making Negatives
“Do” and “does” are forms of the verb “to do.” We use them as auxiliary verbs (also called “helping verbs”) to:
- Ask questions.
- Form negative sentences.
- Emphasize a verb (less common for beginners, but good to know!).
Just like “have” and “has,” the choice between “do” and “does” depends on the subject.
Who uses “Do”?
We use do with:
- I
- You
- We
- They
- Plural nouns
Who uses “Does”?
We use does with:
- He
- She
- It
- Singular nouns
Examples: Asking Questions with “Do/Does”
When forming a question with “do” or “does,” remember this pattern:
Do/Does + Subject + Main Verb (base form) + Rest of the sentence?
Notice that the main verb always stays in its base form (e.g., “go,” “eat,” “play,” not “goes,” “eats,” “plays”).
| Do/Does | Subject | Main Verb | Rest of the Sentence | Example Question |
| Do | I | understand | this? | Do I understand this? |
| Do | you | like | pizza? | Do you like pizza? |
| Do | we | need | more time? | Do we need more time? |
| Do | they | live | here? | Do they live here? |
| Do | the birds | sing | in the morning? | Do the birds sing in the morning? |
| Does | he | play | soccer? | Does he play soccer? |
| Does | she | speak | French? | Does she speak French? |
| Does | it | work | well? | Does it work well? |
| Does | your friend | study | hard? | Does your friend study hard? |
Examples: Making Negative Statements with “Do/Does”
When making a negative statement, we use “do not” (don’t) or “does not” (doesn’t). The main verb also stays in its base form.
Subject + Do/Does + not + Main Verb (base form) + Rest of the sentence.
| Subject | Do/Does | not | Main Verb | Rest of the Sentence | Example Negative Sentence |
| I | do | not | know | the answer. | I do not know the answer. |
| You | do | not | want | coffee. | You do not want coffee. |
| We | do | not | have | much time. | We do not have much time. |
| They | do | not | speak | German. | They do not speak German. |
| He | does | not | like | vegetables. | He does not like vegetables. |
| She | does | not | work | on weekends. | She does not work on weekends. |
| It | does | not | rain | often here. | It does not rain often here. |
| My brother | does | not | play | video games. | My brother does not play video games. |
Chart for “Do” vs. “Does”
| Subject | Use in Questions/Negatives |
| I | do |
| You | do |
| We | do |
| They | do |
| Plural Nouns | do |
| He | does |
| She | does |
| It | does |
| Singular Nouns | does |
Examples:
- I have a dog.
- She has a dog.
- I don’t have a dog.
- She doesn’t have a dog
- My dog (it) has four legs.
- It doesn’t have blue hair.
- Do you have a dog? – Yes, I have a dog. or No I don’t have a dog.
- Does your dog run fast? – Yes, my dog funs fast.
- Does she have a dog? – No, she doesn’t have a dog
3. Don’t vs. Doesn’t: The Short and Sweet Negatives
“Don’t” and “doesn’t” are simply contractions of “do not” and “does not.” Contractions are very common in spoken English and informal writing.
- Don’t = Do not
- Doesn’t = Does not
The rules for when to use “don’t” or “doesn’t” are exactly the same as for “do not” and “does not.”
When to use “Don’t”?
- I don’t like spiders.
- You don’t understand.
- We don’t have much time.
- They don’t live here anymore.
- My friends don’t watch that show.
When to use “Doesn’t”?
- He doesn’t eat meat.
- She doesn’t speak Spanish.
- It doesn’t matter.
- My dog doesn’t bark much.
Examples: “Don’t” and “Doesn’t” in Action
| Subject | Contraction | Main Verb | Rest of the Sentence | Example Sentence |
| I | don’t | want | any more. | I don’t want any more. |
| You | don’t | know | the answer. | You don’t know the answer. |
| We | don’t | usually | go out on Mondays. | We don’t usually go out on Mondays. |
| They | don’t | play | chess. | They don’t play chess. |
| He | doesn’t | like | spicy food. | He doesn’t like spicy food. |
| She | doesn’t | often | visit her family. | She doesn’t often visit her family. |
| It | doesn’t | look | good. | It doesn’t look good. |
| The car | doesn’t | start | easily. | The car doesn’t start easily. |
Additional Helpful Content: Common Mistakes and Tips
- Remember the Base Form! A very common mistake is to change the main verb when using “do/does/don’t/doesn’t.” For example, don’t say “Does he likes pizza?” It should be “Does he like pizza?”
- “Have” with “Do/Does”: You can even use “do/does” to ask questions or make negatives with “have.”
- Do you have a pet? (Correct!)
- Does she have a brother? (Correct!)
- He doesn’t have time. (Correct!)
- (Not: “Does she has a brother?” or “He doesn’t has time.”)
- Practice Makes Perfect! The best way to master these words is to use them! Try writing your own sentences, asking questions to a friend, or even talking to yourself in English.
Quiz Time! (Self-Assessment)
Choose the correct word to complete the sentence:
- I ______ a big family. (have / has)
- ______ she live in New York? (Do / Does)
- We ______ understand the question. (don’t / doesn’t)
- My brother ______ a new phone. (have / has)
- ______ they like to read? (Do / Does)
- The dog ______ eat vegetables. (don’t / doesn’t)
Quiz Answers:
- have
- Does
- don’t
- has
- Do
- doesn’t
Here is a PDF document you can download with 25 practice questions for making sentences using Have/Has, Do/Does, Don’t/Doesn’t. The answers are on a separate sheet.
Additional helpful information
Using Do or Does to form simple English questions – Do and Does: Simple English Questions for Beginners
Study English Modal Verbs, English Possibility – English Modal Verbs: ‘May,’ ‘Might,’ ‘Could’: English Possibility
External Links for Authoritative Sources
For more in-depth explanations and additional practice, check out these reputable English learning resources:
- British Council LearnEnglish: A fantastic resource with clear explanations and exercises for all levels.
- Grammarly Blog: Offers helpful articles on various grammar topics.